-

About
Ruigad (Xiamen) Sanitary Ware Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 and is located in beautiful Xiamen. It is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research and development, production and sales of sanitary products that save global water resources.
-
 Product Center
Product Center
Products
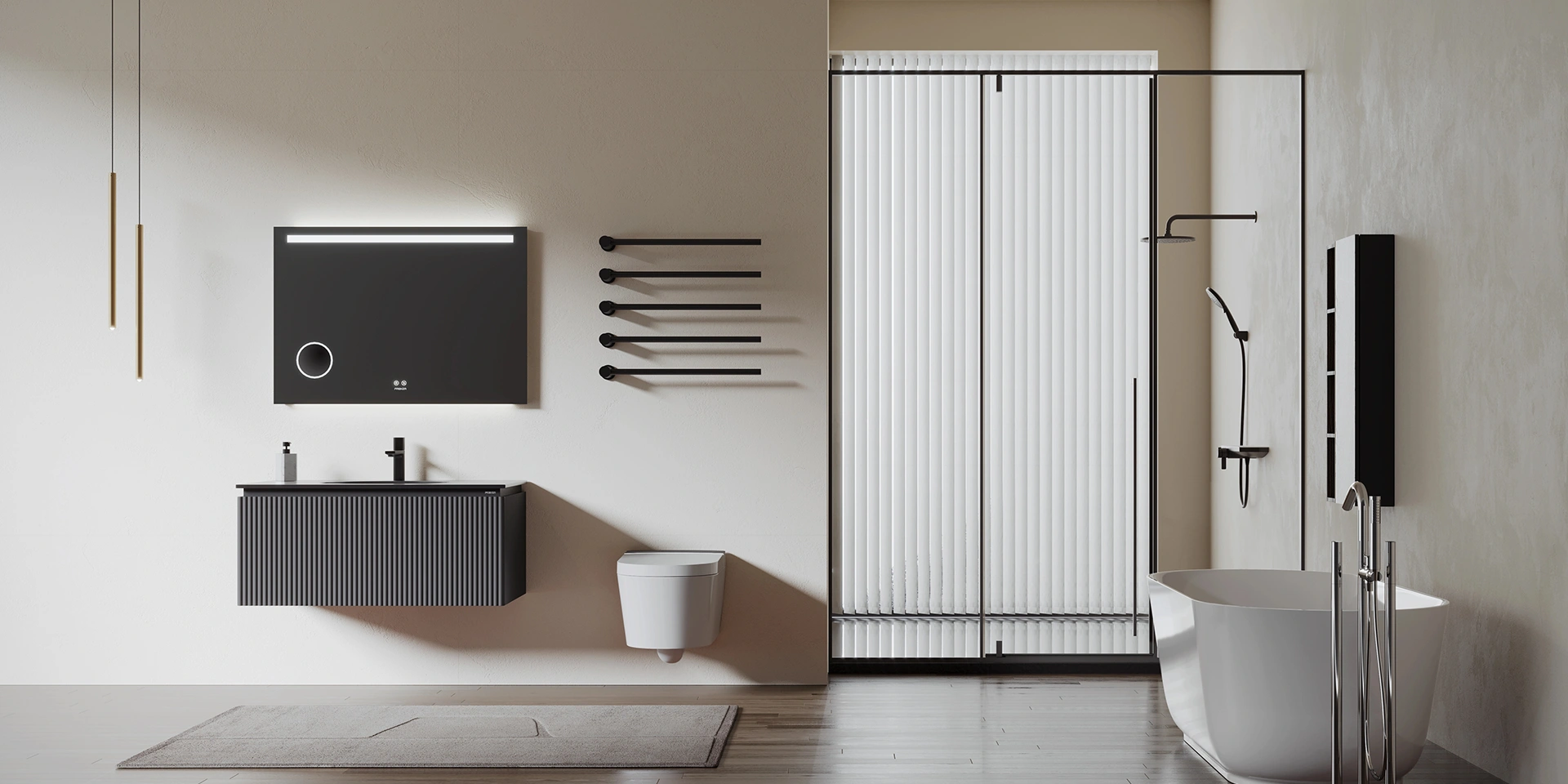
The main production of sanitary products: water-saving water inlet valve and drain valve, electronic induction water tank, intelligent toilet, hidden water tank, hanging water tank, all kinds of drainage pipe fittings, etc., mainly used in residential, hotel, shopping malls, office buildings and other housing buildings toilet facilities, including water-saving water inlet valve and drain valve, hidden water tank is the company's main products.
-
 Solution
Solution
Solution
Mainly used in residential homes, hotels, shopping malls, office buildings and other buildings in the toilet facilities
-
 Core Competitiveness
Core Competitiveness
Core
To create a new concept of Ruigad sanitary ware brand, where there is sanitary ware, there is Ruigad sanitary ware.
-
 News Center
News Center
News
We will not regularly for you to update the bathroom market new trends and share the company's new dynamic.
-
Dedicated to the development of water-saving and intelligent bathroom products
Social responsibility

Social responsibility refers to the responsibility of an organization to the society. An organization should be run and managed in a way that benefits society. Social responsibility usually refers to the organization's social obligations that are higher than the organization's own goals. It goes beyond the legal and economic obligations required by the organization, and social responsibility is the requirement of organizational management ethics, which is entirely a voluntary act of the organization out of obligations.
If an enterprise undertakes not only legal and economic obligations, but also the obligation to "pursue long-term goals that are beneficial to society", we say that the enterprise has social responsibility.
Social responsibility includes corporate environmental protection, safe production, social ethics and public interests, and consists of economic responsibility, sustainable development responsibility, legal responsibility and moral responsibility. This refers not only to corporate responsibility, but also to other social responsibilities.
Social responsibility is the responsibility of the individual to the society as a whole stipulated in social law and economic law, and it is a dual structure system composed of role obligation responsibility and legal responsibility. There are two kinds of responsibilities: the first refers to what should be done within the duty, such as duty, responsibility, post responsibility, etc. This kind of responsibility is actually a kind of role obligation responsibility or expected responsibility. The second is a form of adverse consequences or mandatory obligations, I .e. past liability, such as liability for breach of contract, tort liability, etc., for failure to do their part (failure to fulfil their role obligations) or failure to fulfil their contributory obligations.
The main production of sanitary products: water-saving inlet valve and drain valve, electronic induction water tank, intelligent toilet, hidden water tank, hanging water tank, all kinds of drainage pipe fittings, etc.
Contact Information
0086-592-6363077
169 Xingqian Road, jimei district, Xiamen City, Fujian Province
 Ruigad@Ruigad.com
Ruigad@Ruigad.com
 0592-6363076
0592-6363076